Monumental Questions - Tule Elk
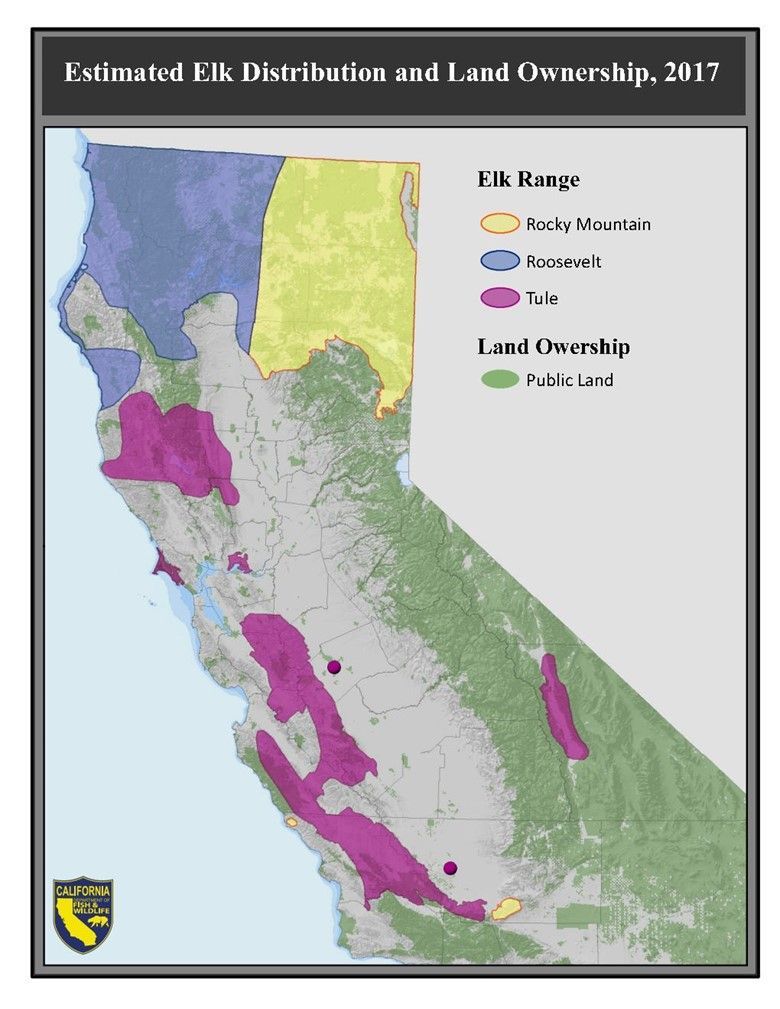
Distribution of Tule Elk in California (CDFW)
Can you tell me more about the herd of Tule Elk I have seen on my way to the Berryessa Snow Mountain National Monument?
California is home to three species of elk: Roosevelt Elk (Cervus elaphus roosevelti), Rocky Mountain Elk (Cervus elaphus nelson) and Tule Elk (Cervus elaphus nannodes). Of the three species, Tule Elk are the smallest. Actually, they are the smallest species of elk found in all of North America. They are also endemic to California which means they are found no where else.
Tule elk bodies are a light buffy brown color with longer, darker hair on their heads and necks but the tell-tale field mark is their flashy white behind. Calves are usually born between May and June but can be born as early as February. They look similar to deer fawn with brown coats and white spots. Adult males, called bulls, average between 450 and 700 pounds but occasionally one can reach about 800 pounds. Adult females, called cows, are about the size of a small male or slightly smaller. Both stand about four to five feet at the shoulder. Interestingly, the yearling males, called “spikes” grow skinny, scrawny antlers (can you guess where their nickname comes from?) during their first year. Males drop their antlers each year and regrow bigger ones the following year. Females do not produce antlers. Tule Elk are highly social and females, calves and “spikes” tend to hang out together in groups of 15-20. Bulls are solitary until about August through October when breeding season, or rut, begins. Calves will remain with their mothers until about the age of two and then they become mature members of the herd. The herds will shift locations based on weather and food availability.
Historically the range of the Tule Elk included most of the Central Valley, from the foothills of the Sierra Nevada west to the coast line, and from southern Shasta County south to the Tehachapi Mountains. It was estimated that there were about 500,000 Tule Elk in California around the early 1800’s but by 1870 habitat loss and over-hunting diminished the population to only two breeding pairs near Buena Vista Lake in Kern County. In 1873, a law was passed to protect them but at that time, it wasn’t clear if any even remained.
In 1874, Henry Miller, a farmer, was draining a marsh to convert it to agricultural fields and discovered a handful of Tule Elk on his property. He recognized their significance and protected the last few elk. Over the next thirty years, the tiny herd grew to 140 individuals. As their numbers increased, Miller asked for help relocating some of the animals to other areas of California as the larger herd size began damaging his fields and fences. At first the relocations were not successful but as methods improved, Tule Elk began to re-establish some areas of their historic range. Between 1914 and 1934, 235 Tule Elk were relocated, including the ancestors of the present-day Cache Creek herd!
Today, Tule Elk numbers are estimated to be about 5,700 in several herds throughout California.
-Kristie Ehrhardt; kehrhardt@tuleyome.org
Tuleyome Land Conservation Program Manager
If you have questions about Berryessa Snow Mountain National Monument that you would like us to address, please email them to Nate Lillge (nlillge@tuleyome.org) or Kristie Ehrhardt (kehrhardt@tuleyome.org).
RECENT ARTICLES






